 |
| November 13, 2018 | Volume 14 Issue 42 |
Motion Control News & Products
Designfax weekly eMagazine
Archives
Partners
Manufacturing Center
Product Spotlight
Modern Applications News
Metalworking Ideas For
Today's Job Shops
Tooling and Production
Strategies for large
metalworking plants
Overhung load adaptors provide load support and contamination protection
 Overhung load adaptors (OHLA) provide both overhung radial and axial load support to protect electrified mobile equipment motors from heavy application loads, extending the lifetime of the motor and alleviating the cost of downtime both from maintenance costs and loss of production. They seal out dirt, grime, and other contaminants too. Zero-Max OHLAs are available in an extensive offering of standard models (including Extra-Duty options) for typical applications or customized designs.
Overhung load adaptors (OHLA) provide both overhung radial and axial load support to protect electrified mobile equipment motors from heavy application loads, extending the lifetime of the motor and alleviating the cost of downtime both from maintenance costs and loss of production. They seal out dirt, grime, and other contaminants too. Zero-Max OHLAs are available in an extensive offering of standard models (including Extra-Duty options) for typical applications or customized designs.
Learn more.
Why choose electric for linear actuators?
 Tolomatic has been delivering a new type of linear motion technology that is giving hydraulics a run for its money. Learn the benefits of electric linear motion systems, the iceberg principle showing total cost of ownership, critical parameters of sizing, and conversion tips.
Tolomatic has been delivering a new type of linear motion technology that is giving hydraulics a run for its money. Learn the benefits of electric linear motion systems, the iceberg principle showing total cost of ownership, critical parameters of sizing, and conversion tips.
Get this informative e-book. (No registration required)
New AC hypoid inverter-duty gearmotors
 Bodine Electric Company introduces 12 new AC inverter-duty hypoid hollow shaft gearmotors. These type 42R-25H2 and 42R-30H3 drives combine an all-new AC inverter-duty, 230/460-VAC motor with two hypoid gearheads. When used with an AC inverter (VFD) control, these units deliver maintenance-free and reliable high-torque output. They are ideal for conveyors, gates, packaging, and other industrial automation equipment that demands both high torque and low power consumption from the driving gearmotor.
Bodine Electric Company introduces 12 new AC inverter-duty hypoid hollow shaft gearmotors. These type 42R-25H2 and 42R-30H3 drives combine an all-new AC inverter-duty, 230/460-VAC motor with two hypoid gearheads. When used with an AC inverter (VFD) control, these units deliver maintenance-free and reliable high-torque output. They are ideal for conveyors, gates, packaging, and other industrial automation equipment that demands both high torque and low power consumption from the driving gearmotor.
Learn more.
Next-gen warehouse automation: Siemens, Universal Robots, and Zivid partner up
 Universal Robots, Siemens, and Zivid have created a new solution combining UR's cobot arms with Siemens' SIMATIC Robot Pick AI software and Zivid's 3D sensors to create a deep-learning picking solution for warehouse automation and intra-logistics fulfillment. It works regardless of object shape, size, opacity, or transparency and is a significant leap in solving the complex challenges faced by the logistics and e-commerce sectors.
Universal Robots, Siemens, and Zivid have created a new solution combining UR's cobot arms with Siemens' SIMATIC Robot Pick AI software and Zivid's 3D sensors to create a deep-learning picking solution for warehouse automation and intra-logistics fulfillment. It works regardless of object shape, size, opacity, or transparency and is a significant leap in solving the complex challenges faced by the logistics and e-commerce sectors.
Read the full article.
Innovative DuoDrive gear and motor unit is UL/CSA certified
 The DuoDrive integrated gear unit and motor from NORD DRIVE-SYSTEMS is a compact, high-efficiency
solution engineered for users in the fields of intralogistics, pharmaceutical, and the food and beverage industries. This drive combines a IE5+ synchronous motor and single-stage helical gear unit into one compact housing with a smooth, easy-to-clean surface. It has a system efficiency up to 92% and is available in two case sizes with a power range of 0.5 to 4.0 hp.
The DuoDrive integrated gear unit and motor from NORD DRIVE-SYSTEMS is a compact, high-efficiency
solution engineered for users in the fields of intralogistics, pharmaceutical, and the food and beverage industries. This drive combines a IE5+ synchronous motor and single-stage helical gear unit into one compact housing with a smooth, easy-to-clean surface. It has a system efficiency up to 92% and is available in two case sizes with a power range of 0.5 to 4.0 hp.
Learn more.
BLDC flat motor with high output torque and speed reduction
 Portescap's 60ECF brushless DC slotted flat motor is the newest frame size to join its flat motor portfolio. This 60-mm BLDC motor features a 38.2-mm body length and an outer-rotor slotted configuration with an open-body design, allowing it to deliver improved heat management in a compact package. Combined with Portescap gearheads, it delivers extremely high output torque and speed reduction. Available in both sensored and sensorless options. A great choice for applications such as electric grippers and exoskeletons, eVTOLs, and surgical robots.
Portescap's 60ECF brushless DC slotted flat motor is the newest frame size to join its flat motor portfolio. This 60-mm BLDC motor features a 38.2-mm body length and an outer-rotor slotted configuration with an open-body design, allowing it to deliver improved heat management in a compact package. Combined with Portescap gearheads, it delivers extremely high output torque and speed reduction. Available in both sensored and sensorless options. A great choice for applications such as electric grippers and exoskeletons, eVTOLs, and surgical robots.
Learn more and view all the specs.
Application story: Complete gearbox and coupling assembly for actuator system
 Learn how GAM engineers not only sized and selected the appropriate gear reducers and couplings required to drive two ball screws in unison using a single motor, but how they also designed the mounting adapters necessary to complete the system. One-stop shopping eliminated unnecessary components and resulted in a 15% reduction in system cost.
Learn how GAM engineers not only sized and selected the appropriate gear reducers and couplings required to drive two ball screws in unison using a single motor, but how they also designed the mounting adapters necessary to complete the system. One-stop shopping eliminated unnecessary components and resulted in a 15% reduction in system cost.
Read this informative GAM blog.
Next-gen motor for pump and fan applications
 The next evolution of the award-winning Aircore EC motor from Infinitum is a high-efficiency system designed to power commercial and industrial applications such as HVAC fans, pumps, and data centers with less energy consumption, reduced emissions, and reduced waste. It features an integrated variable frequency drive and delivers upward of 93% system efficiency, as well as class-leading power and torque density in a low-footprint package that is 20% lighter than the previous version. Four sizes available.
The next evolution of the award-winning Aircore EC motor from Infinitum is a high-efficiency system designed to power commercial and industrial applications such as HVAC fans, pumps, and data centers with less energy consumption, reduced emissions, and reduced waste. It features an integrated variable frequency drive and delivers upward of 93% system efficiency, as well as class-leading power and torque density in a low-footprint package that is 20% lighter than the previous version. Four sizes available.
Learn more.
Telescoping linear actuators for space-constrained applications
 Rollon's new TLS telescoping linear actuators enable long stroke lengths with minimal closed lengths, which is especially good for applications with minimal vertical clearance. These actuators integrate seamlessly into multi-axis systems and are available in two- or three-stage versions. Equipped with a built-in automated lubrication system, the TLS Series features a synchronized drive system, requiring only a single motor to achieve motion. Four sizes (100, 230, 280, and 360) with up to 3,000-mm stroke length.
Rollon's new TLS telescoping linear actuators enable long stroke lengths with minimal closed lengths, which is especially good for applications with minimal vertical clearance. These actuators integrate seamlessly into multi-axis systems and are available in two- or three-stage versions. Equipped with a built-in automated lubrication system, the TLS Series features a synchronized drive system, requiring only a single motor to achieve motion. Four sizes (100, 230, 280, and 360) with up to 3,000-mm stroke length.
Learn more.
Competitively priced long-stroke parallel gripper
 The DHPL from Festo is a new generation of pneumatic long-stroke grippers that offers a host of advantages for high-load and high-torque applications. It is interchangeable with competitive long-stroke grippers and provides the added benefits of lighter weight, higher precision, and no maintenance. It is ideal for gripping larger items, including stacking boxes, gripping shaped parts, and keeping bags open. It has high repetition accuracy due to three rugged guide rods and a rack-and-pinion design.
The DHPL from Festo is a new generation of pneumatic long-stroke grippers that offers a host of advantages for high-load and high-torque applications. It is interchangeable with competitive long-stroke grippers and provides the added benefits of lighter weight, higher precision, and no maintenance. It is ideal for gripping larger items, including stacking boxes, gripping shaped parts, and keeping bags open. It has high repetition accuracy due to three rugged guide rods and a rack-and-pinion design.
Learn more.
Extend your range of motion: Controllers for mini motors
 FAULHABER has added another extremely compact Motion Controller without housing to its product range. The new MC3603 controller is ideal for integration in equipment manufacturing and medical tech applications. With 36 V and 3 A (peak current 9 A), it covers the power range up to 100 W and is suitable for DC motors with encoder, brushless drives, or linear motors.
FAULHABER has added another extremely compact Motion Controller without housing to its product range. The new MC3603 controller is ideal for integration in equipment manufacturing and medical tech applications. With 36 V and 3 A (peak current 9 A), it covers the power range up to 100 W and is suitable for DC motors with encoder, brushless drives, or linear motors.
Learn more.
When is a frameless brushless DC motor the right choice?
 Frameless BLDC motors fit easily into small, compact machines that require high precision, high torque, and high efficiency, such as robotic applications where a mix of low weight and inertia is critical. Learn from the experts at SDP/SI how these motors can replace heavier, less efficient hydraulic components by decreasing operating and maintenance costs. These motors are also more environmentally friendly than others.
Frameless BLDC motors fit easily into small, compact machines that require high precision, high torque, and high efficiency, such as robotic applications where a mix of low weight and inertia is critical. Learn from the experts at SDP/SI how these motors can replace heavier, less efficient hydraulic components by decreasing operating and maintenance costs. These motors are also more environmentally friendly than others.
View the video.
Tiny and smart: Step motor with closed-loop control
 Nanotec's new PD1-C step motor features an integrated controller and absolute encoder with closed-loop control. With a flange size of merely 28 mm (NEMA 11), this compact motor reaches a max holding torque of 18 Ncm and a peak current of 3 A. Three motor versions are available: IP20 protection, IP65 protection, and a motor with open housing that can be modified with custom connectors. Ideal for applications with space constraints, effectively reducing both wiring complexity and installation costs.
Nanotec's new PD1-C step motor features an integrated controller and absolute encoder with closed-loop control. With a flange size of merely 28 mm (NEMA 11), this compact motor reaches a max holding torque of 18 Ncm and a peak current of 3 A. Three motor versions are available: IP20 protection, IP65 protection, and a motor with open housing that can be modified with custom connectors. Ideal for applications with space constraints, effectively reducing both wiring complexity and installation costs.
Learn more.
Closed loop steppers drive new motion control applications
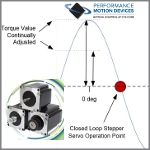 According to the motion experts at Performance Motion Devices, when it comes to step motors, the drive technique called closed loop stepper is making everything old new again and driving a burst of interest in the use of two-phase step motors. It's "winning back machine designers who may have relegated step motors to the category of low cost but low performance."
According to the motion experts at Performance Motion Devices, when it comes to step motors, the drive technique called closed loop stepper is making everything old new again and driving a burst of interest in the use of two-phase step motors. It's "winning back machine designers who may have relegated step motors to the category of low cost but low performance."
Read this informative Performance Motion Devices article.
Intelligent compact drives with extended fieldbus options
 The intelligent PD6 compact drives from Nanotec are now available with Profinet and EtherNet/IP. They combine motor, controller, and encoder in a space-saving package. With its 80-mm flange and a rated power of 942 W, the PD6-EB is the most powerful brushless DC motor of this product family. The stepper motor version has an 86-mm flange (NEMA 34) and a holding torque up to 10 Nm. Features include acceleration feed forward and jerk-limited ramps. Reduced installation time and wiring make the PD6 series a highly profitable choice for machine tools, packaging machines, or conveyor belts.
The intelligent PD6 compact drives from Nanotec are now available with Profinet and EtherNet/IP. They combine motor, controller, and encoder in a space-saving package. With its 80-mm flange and a rated power of 942 W, the PD6-EB is the most powerful brushless DC motor of this product family. The stepper motor version has an 86-mm flange (NEMA 34) and a holding torque up to 10 Nm. Features include acceleration feed forward and jerk-limited ramps. Reduced installation time and wiring make the PD6 series a highly profitable choice for machine tools, packaging machines, or conveyor belts.
Learn more.
Researchers say impact of WWII bombing raids felt at edge of space
Bombing raids by Allied forces during the Second World War not only caused devastation on the ground but also sent shockwaves through Earth's atmosphere that were detected at the edge of space, according to new research. University of Reading researchers in England have revealed the shockwaves produced by huge bombs dropped by Allied planes on European cities were big enough to weaken the electrified upper atmosphere -- the ionosphere -- above the U.K., 1,000 km away. The results were published Sept. 25 in the European Geosciences Union journal Annales Geophysicae.
Scientists are using the findings to further understanding of how natural forces from below, like lightning, volcanic eruptions, and earthquakes, affect Earth's upper atmosphere.

Bombing of a factory at Marienburg, Germany, on Oct. 9, 1943. [Credit: U.S. Air Force]
Chris Scott, Professor of Space and Atmospheric Physics, said: "The images of neighborhoods across Europe reduced to rubble due to wartime air raids are a lasting reminder of the destruction that can be caused by man-made explosions. But the impact of these bombs way up in the Earth's atmosphere has never been realized until now."
"It is astonishing to see how the ripples caused by man-made explosions can affect the edge of space. Each raid released the energy of at least 300 lightning strikes. The sheer power involved has allowed us to quantify how events on the Earth's surface can also affect the ionosphere."
In the study, researchers looked at daily records at the Radio Research Center in Slough, U.K., collected between 1943-45. Sequences of radio pulses over a range of shortwave frequencies were sent 100 to 300 km above the Earth's surface to reveal the height and electron concentration of ionization within the upper atmosphere.
The strength of the ionosphere is known to be strongly influenced by solar activity, but the ionosphere is far more variable than can be explained by current modeling. The ionosphere affects modern technologies such as radio communications, GPS systems, radio telescopes, and some early warning radar, however the extent of the impact on radio communications during the Second World War is unclear.
Researchers studied the ionosphere response records around the time of 152 large Allied air raids in Europe and found the electron concentration significantly decreased due to the shockwaves caused by the bombs detonating near the Earth's surface. This is thought to have heated the upper atmosphere, enhancing the loss of ionization.
Although the London "Blitz" bombing was much closer to Slough, the continuous nature of these attacks and the fact there is far less surviving information about them made it more challenging to separate the impact of these explosions from natural seasonal variation.
Detailed records of the Allied raids reveal their four-engine planes routinely carried much larger bombs than the German Luftwaffe's two-engine planes could. These included the "Grand Slam," which weighed up to 10 tons.
Professor Patrick Major, University of Reading historian and a co-author of the study, said: "Aircrew involved in the raids reported having their aircraft damaged by the bomb shockwaves, despite being above the recommended height. Residents under the bombs would routinely recall being thrown through the air by the pressure waves of air mines exploding, and window casements and doors would be blown off their hinges. There were even rumors that wrapping wet towels around the face might save those in shelters from having their lungs collapsed by blast waves, which would leave victims otherwise externally untouched."
"The unprecedented power of these attacks has proved useful for scientists to gauge the impact such events can have hundreds of kilometers above the Earth, in addition to the devastation they caused on the ground."
The researchers now need members of the public to help digitize more early atmospheric data to help understand the impact of the many hundreds of smaller bombing raids during the war, and to help determine the minimum explosive energy required to trigger a detectable response in the ionosphere.
Source: European Geosciences Union
Published November 2018
Rate this article
View our terms of use and privacy policy

